Simon Giebenhain
PhD Student, Technical University of Munich
About Me
I am a PhD student at the Technical University of Munich at the Niessnerlab. My general areas of interest are machine learning and computer vision. More specifically, I am highly interested in virtual avatars, generative models and dynamic scene representations. I am on the search for the right amount of domain specific inductive biases in heavily data-driven transformer-based solutions. Previously I recieved my master’s degree at the University of Konstanz under the supervision of Prof. Bastian Goldlücke.
I will enter the job market soon. Starting to search for research scientist positions, or interesting start-ups.

Publications

Modern, data-driven approach to approach single-image 3D face reconstruction using ViT networks, pixel-aligned geonmetric pretraining and large scale mixed-2D-3D training.
Simon Giebenhain, Tobias Kirschstein, Liam Schoneveld, Davide Davoli, Zhe Chen, Matthias Nießner
![]()
Single-image 3DGS-based avatar prediction. Gaussian parameters are predicted in canonical space using a transformer, animation is learned using cross attention to Pixel3DMM estimated FLAME expression codes.
Tobias Kirschstein, Simon Giebenhain, Matthias Nießner
![]()
3DMM tracking using ViT predictions for pixel-aligned geometric cues, i.e. uv-coordinates and surface normals. Extreme generalization due to DINOv2 backbone.
Simon Giebenhain, Tobias Kirschstein, Martin Rünz, Lourdes Agapito, Matthias Nießner
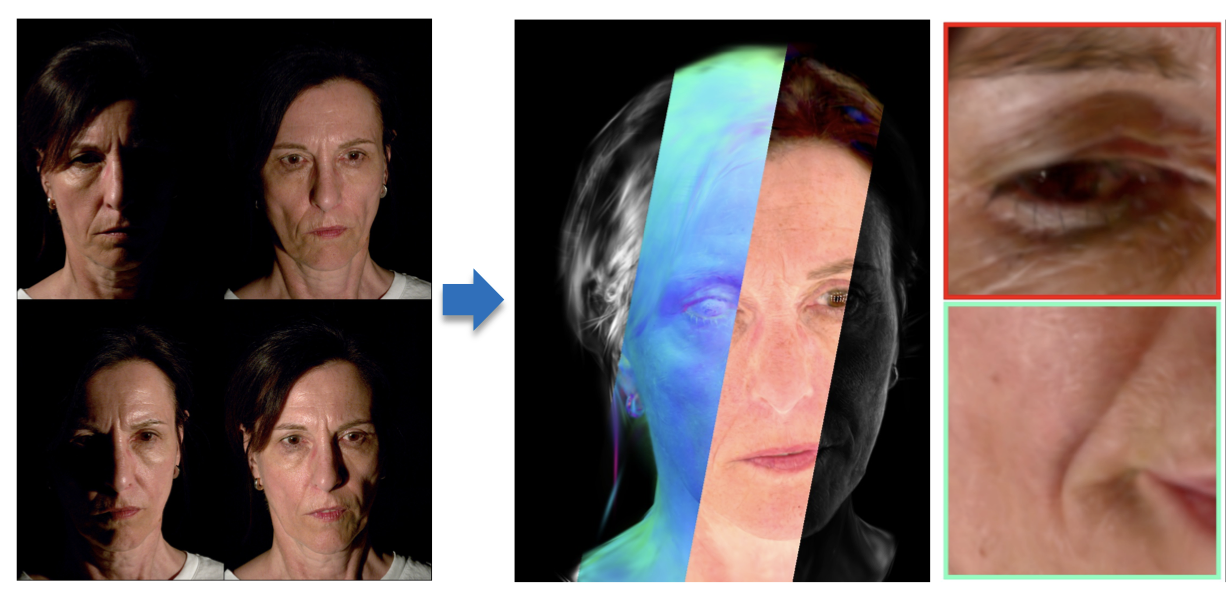

Highest-quality publicly-available light stage data, and method to create relightable Gaussian avatars using a hypbrid between classical-CG and learned shading.
Jonathan SChmidt, Simon Giebenhain, Matthias Nießner
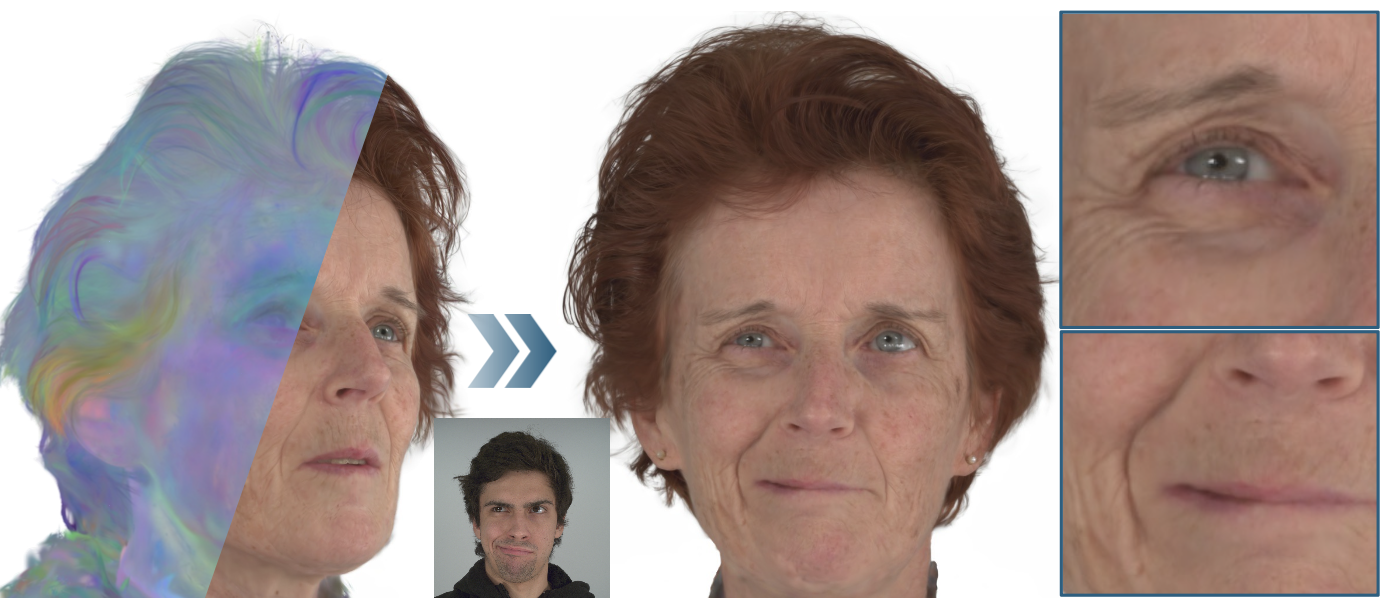
High-quality, photo-realistic 3DGS-based avatars from multi-view video recordings, using MonoNPHM instead of FLAME.
Simon Giebenhain, Tobias Kirschstein, Martin Rünz, Lourdes Agapito, Matthias Nießner
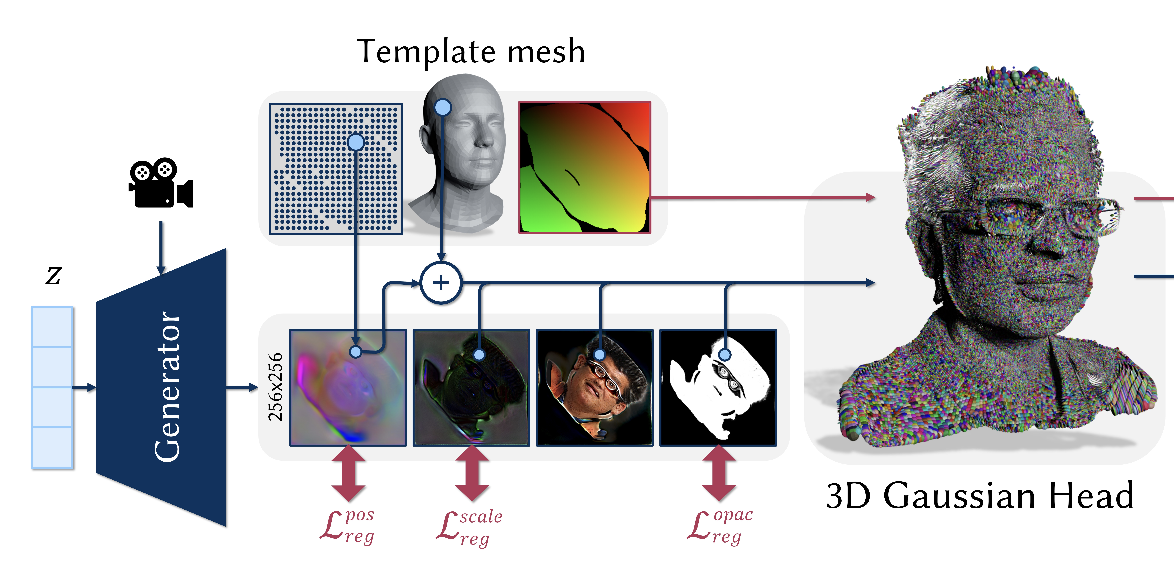
EG3D-style GAN to predict 3DGS-parameters in UV-space, learned purely from 2D image collections with camera annotations
Tobias Kirschstein, Simon Giebenhain, Jiapeng Tang, Markos Georgopoulos, Matthias Nießner

MonoNPHM is a neural parametric head model that disentangles geomery, appearance and facial expression into three separate latent spaces. Using MonoNPHM as a prior, we tackle the task of dynamic 3D head reconstruction from monocular RGB videos, using inverse, SDF-based, volumetric rendering.
Simon Giebenhain, Tobias Kirschstein, Markos Georgopoulos, Martin Rünz, Lourdes Agapito, Matthias Nießner
![]()
DiffusionAvatar uses diffusion-based, deferred neural rendering to translate geometric cues from an underlying neural parametric head model (NPHM) to photo-realistic renderings. The underlying NPHM prvides accurate control over facial expressions, while the deferred neural rendering leverages the 2D prior of StableDiffusion, in order to generate compeeling images.
Tobias Kirschstein, Simon Giebenhain, Matthias Nießner
NeRSemble reconstructs high-fidelity dynamic-radiance fields of human heads. We combine a deformation for coarse movments with an ensemble of 3D multi-resolution hash encodings, which act as a form of expression dependent volumetric texture that models fine-grained, expression-depndent details. Additionally we propose a new 16 camera multi-view capture dataset (7.1 MP resolution and 73 frames per second) containing 4700 sequences of more than 220 human subjects.
Tobias Kirschstein, Shenhan Qian, Simon Giebenhain, Tim Walter, Matthias Nießner

NPHM is a field-based Neural parametric model for human heads, that represents identity geometry implicitly in a cononical space and models expressions as forward deformations. The SDF in canonical field is represented as an ensemble of local MLPs centered around facial anchor points. To train our model we capture a large dataset of complete head geometry containing over 250 people in 23 expressions each using high quality structured light scanners.
Simon Giebenhain, Tobias Kirschstein, Markos Georgopoulos, Martin Rünz, Lourdes Agapito, Matthias Nießner

In Neural Puppeteer (NePu) we explore single-evaluation-per-pixel neural rendering for dynamic objects. In particular we learn a latent space that relates the 3D pose of an object with multiple renderable properties, such as occupancy masks, color and depth. The fast rendering speed allows us to tackle 3D keypoint detection by inverse rendering from multi-view sillhouettes. Using silhouettes alone, we obtain an appearance and lightning invariant representation, that we can fit to real images, in a zero-shot-synthtetic-to-real scenario.
Simon Giebenhain*, Urs Waldmann*, Ole Johannsen, and Bastian Goldluecke
More information on our Project Page.
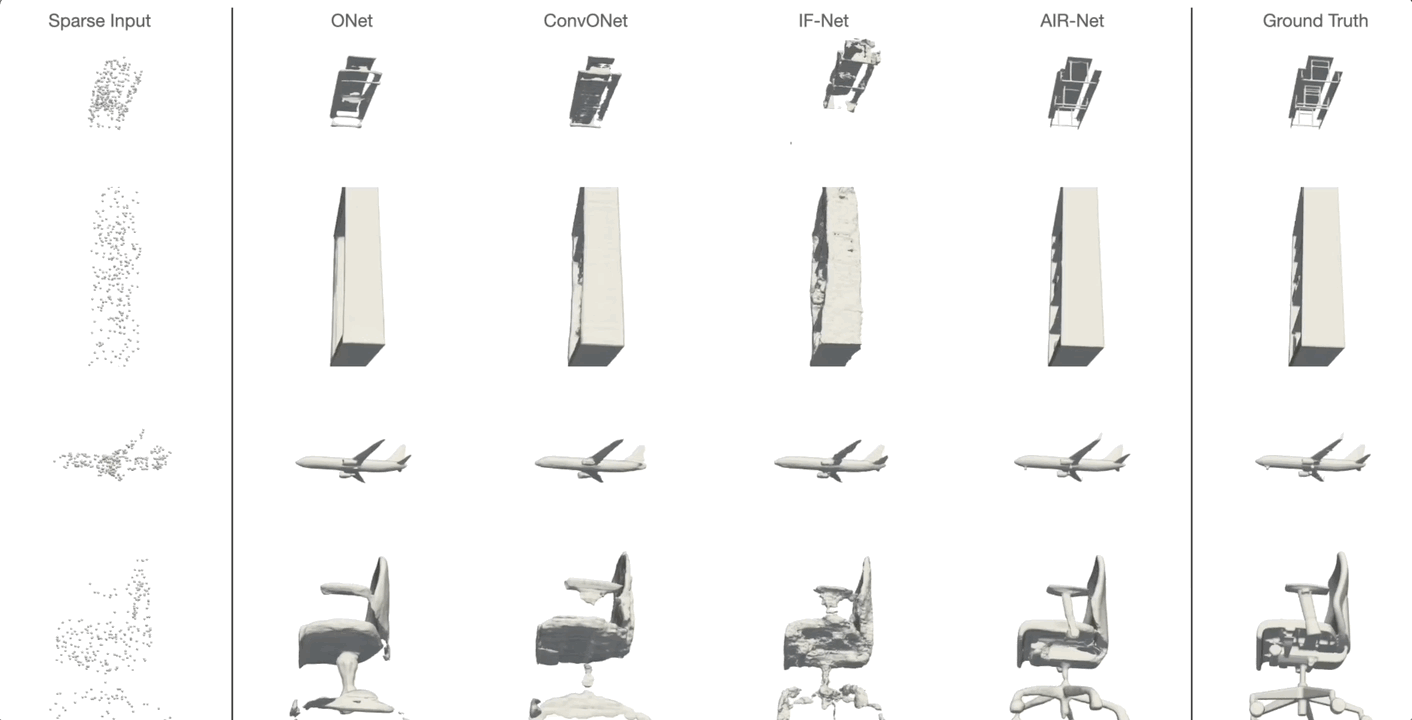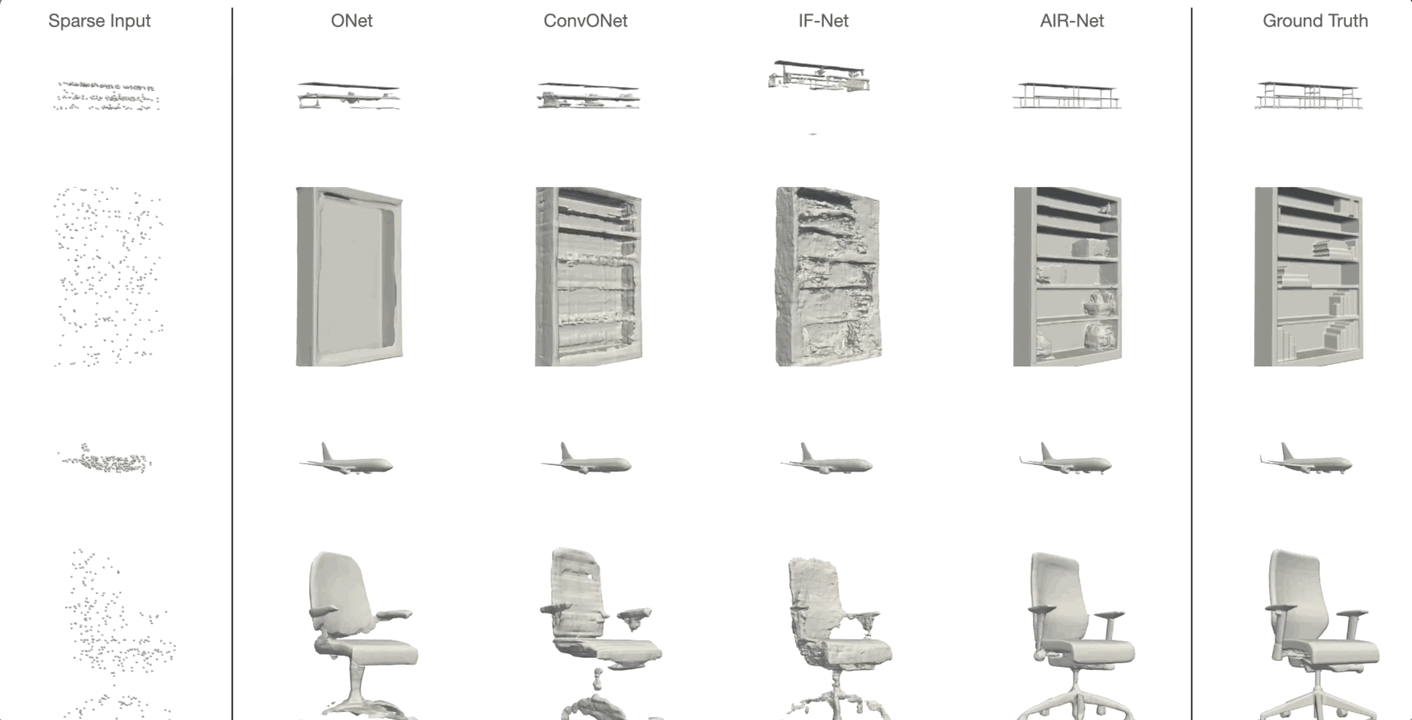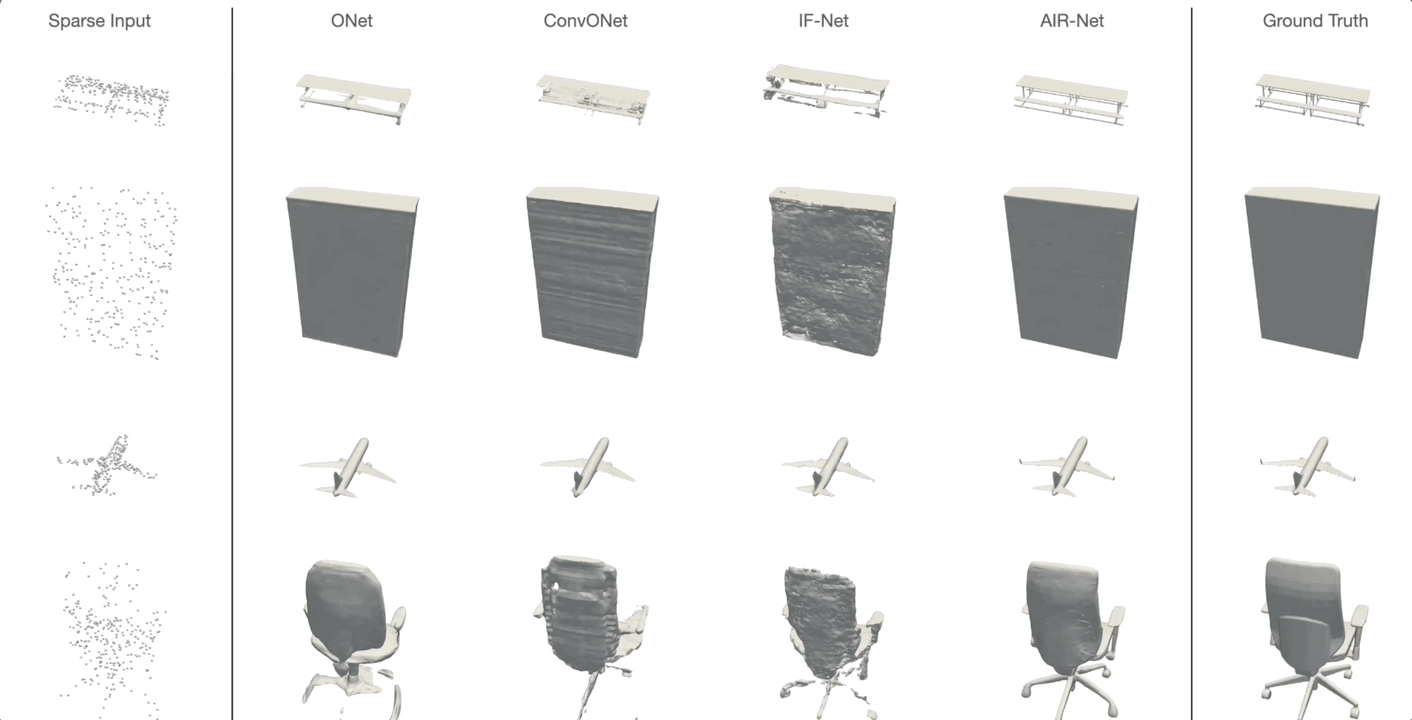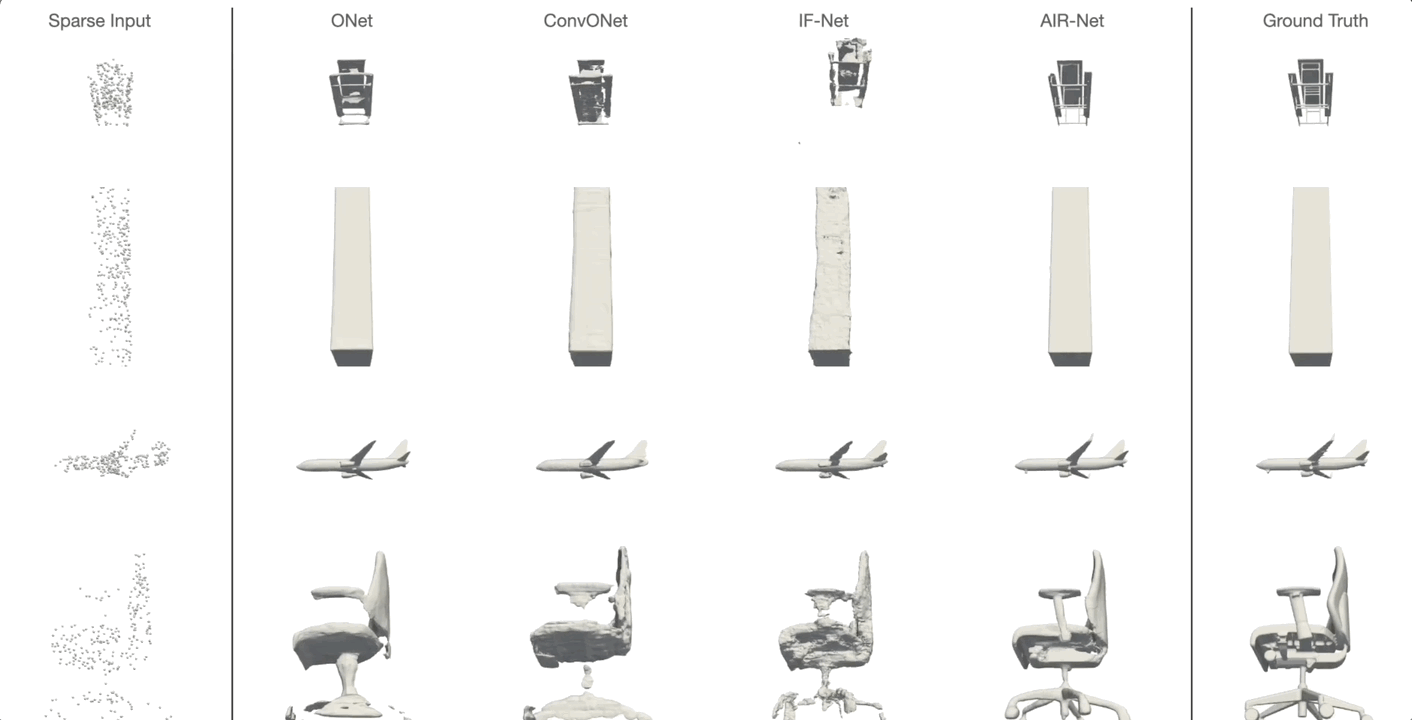
AIR-Net is the first encoder-based, grid-free, local and implicit shape representation model. Our network design focuses on conformity with geometric properties like permutation invariance and translation equivariance of the point cloud. Furthermore, our network operates on the k-nearest-neighbor graph, which encodes an effective and efficient inductive bias. Using an expressive decoder, we are able to condition an implicit function on a sparse set of local latent vectors. While this simple latent representation certainly offers exciting avenues for future work, our model already outperforms the previous state-of-the-art.
Simon Giebenhain and Bastian Goldlücke
IEEE International Conference on 3D Vision (2021)
Code available here.
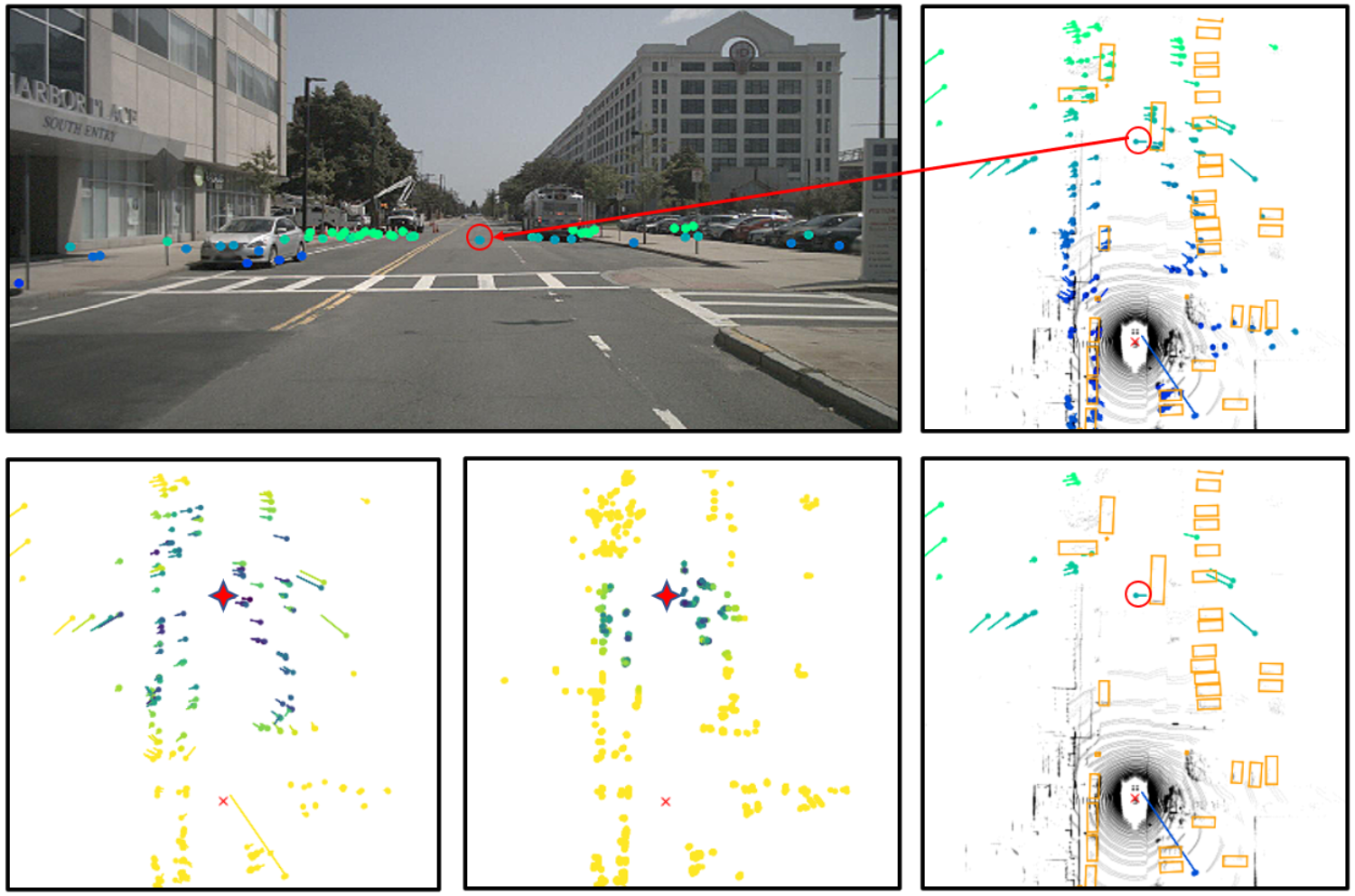
The safety of autonmous vehicles is heavily dependent on the reliability of its underlying sensor measurements. While radar is often overlooked, its all-day, all-weather and long-range capabilities, as well as, low price render it a promising candidate. In this paper we introduce an attention based sensor-fusion method, to filter out false-positive detections (so called ghost targets) in radar.
LeiChen Wang, Simon Giebenhain, Carsten Anklam, Bastian Goldlücke
IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters (2021)
